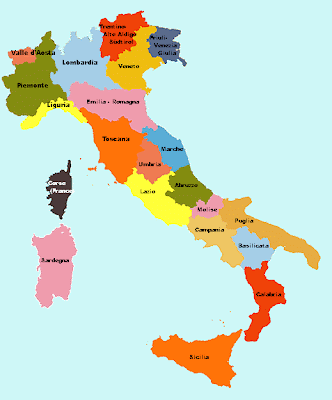
 Italy /ˈɪtəli/ (help·info) (Italian: Italia), officially the Italian Republic (Italian: Repubblica Italiana), is a country located on the Italian Peninsula in Southern Europe and on the two largest islands in the Mediterranean Sea, Sicily and Sardinia. Italy shares its northern, Alpine boundary with France, Switzerland, Austria and Slovenia. The independent states of San Marino and the Vatican City are enclaves within the Italian Peninsula, and Campione d'Italia is an Italian exclave in Switzerland.
Italy /ˈɪtəli/ (help·info) (Italian: Italia), officially the Italian Republic (Italian: Repubblica Italiana), is a country located on the Italian Peninsula in Southern Europe and on the two largest islands in the Mediterranean Sea, Sicily and Sardinia. Italy shares its northern, Alpine boundary with France, Switzerland, Austria and Slovenia. The independent states of San Marino and the Vatican City are enclaves within the Italian Peninsula, and Campione d'Italia is an Italian exclave in Switzerland.The land known as Italy today has been the cradle of many European cultures and peoples, such as the Etruscans and the Romans, and later was the birthplace of the University, the Renaissance that began in Tuscany and spread all over Europe, Vitruvian Man, modern science and astronomy, heliocentrism and opera. Italy's capital, Rome, was for centuries the center of Western civilization. Italy possessed a colonial empire from the second half of the nineteenth century to the mid-twentieth century.
Today, Italy is a democratic republic and a developed country with the eighth-highest quality of life index rating in the world.[6] It is a founding member of what is now the European Union, having signed the Treaty of Rome in 1957, and it is a founding member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). It is a member of the G8, having the world's seventh-largest nominal GDP, and is also a member state of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the World Trade Organization (WTO), the Council of Europe, the Western European Union, and the Central European Initiative. Italy is a Schengen state. It has the world's seventh-largest defence budget and shares NATO's nuclear weapons. On 1 January 2007, Italy began a two-year term as a non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council.

Capital(and largest city)
Rome 41°54′N 12°29′E / 41.9°N 12.483°E / 41.9; 12.483
Official languages
Italian1
Ethnic groups ([1])
94.2% Italian1.94% Romanian, Albanian, Ukrainian1.34% African0.92% Asian0.46% South American1.14% Other
Demonym
Italian
Government
Parliamentary republic
-
President
Giorgio Napolitano
-
Prime Minister
Silvio Berlusconi
Legislature
Parliament
-
Upper House
Senate
-
Lower House
Chamber of Deputies
Formation
-
Unification
17 March 1861
-
Republic
2 June 1946
EU accession
25 March 1957 (founding member)
Area
-
Total
301,338 km2 (71st)116,346 sq mi
-
Water (%)
2.4
Population
-
2008 estimate
60,067,554[2] (23rd)
-
2001 census
57,110,144
-
Density
199.3/km2 (54th)516.3/sq mi
GDP (PPP)
2009 estimate
-
Total
$1,815 billion[3] (10th)
-
Per capita
$29,273[3] (27th)
GDP (nominal)
2009 estimate
-
Total
$2.314 billion[3] (7th)
-
Per capita
$33,253[3] (21st)
Gini (2000)
36 (medium)
HDI (2006)
▲ 0.945[4] (high) (19th)
Currency
Euro (€)2 (EUR)
Time zone
CET (UTC+1)
-
Summer (DST)
CEST (UTC+2)
Drives on the
right
Internet TLD
.it3
Calling code
39
Germany comprises 16 states (Bundesländer)